Financial Accounting Standards
Share this Post
Related posts
Financial Accounting Standards Board History
FEBRUARY 22, 2026
Since 1973, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) has been the designated organisation in the private sector for…
Read MoreFinancial Accounting Standards No. 5
FEBRUARY 22, 2026
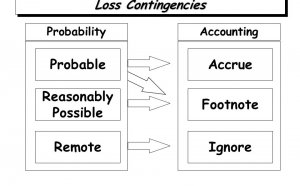
Presentation Chapter 13-1 Current Liabilities and Contingencies
Read More